Does an Enzyme Change the Delta G of a Reaction
Enthalpy denoted H and measured in Jmol is total energy. The activation energy is the difference in free energy between the substrate and the transition state.

Enzymes Effect On Activation Energy And Free Energy Youtube
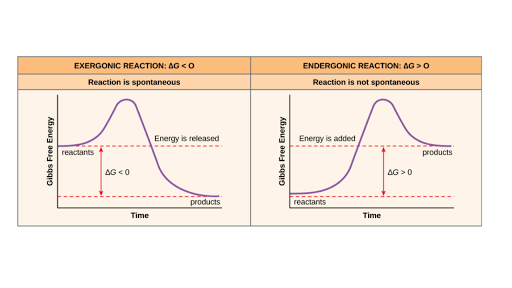
Endergonic reactions require an input of energy.
. It cannot make an endergonic reaction exergonic. Enzymes do affect the activation energy. Standard free energy change Delta G0.
Therefore the delta G stays the same. An enzyme cannot change the Delta G for a reaction. Free energy of activation refers to Gibbs free energy.
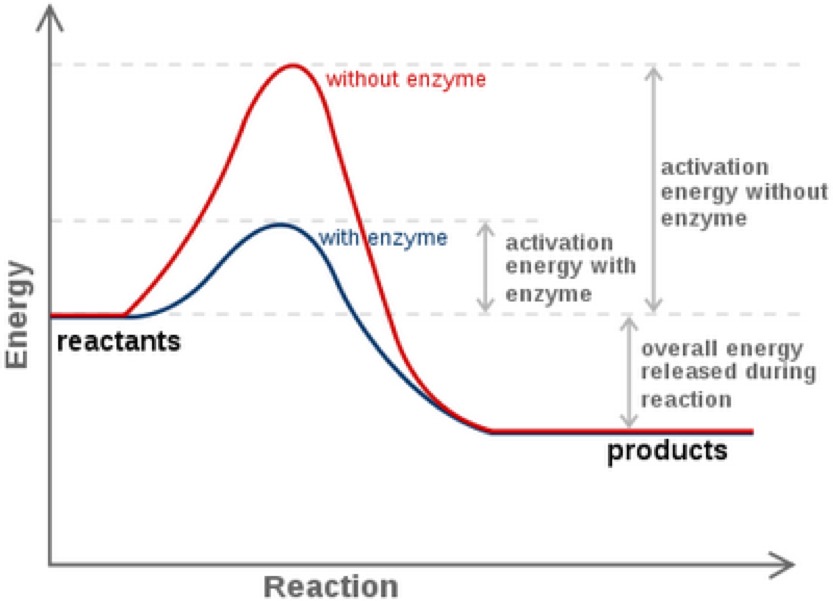
Enzymes only change the activation energy or the kinetic pathway the reaction proceeds through. It does not affect the energy of the reactants and the products. What does an enzyme change in a reaction.
What happens to Delta G when enzyme is doubled. -Although enzymes can INCREASE the RATE of reactions they CANNOT alter the overall DELTA G for a reaction. And usually this energy value is much higher than the free energy change for the reaction which is why enzymes speed up a reaction by lowering the reactions activation energy.
The types of products. If you double the amount of enzyme present the delta G of a reaction will not change. How does an enzyme catalyze a reaction.
This increases the reaction rate. Do enzymes alter the delta G. NO The presence of an enzyme does not affect the overall energy change ΔG or change the energy of the reactants or products.
As the rxn goes towards equilibrium delta G without the naught changes because the rxn is proceeding. Reduces the activation energy D. Standard free energy change at STP-STP H1 Delta G0.
What happens to Delta G when enzyme is doubled. Enzymes decrease the Gibbs free energy of activation but they have no effect on the free energy of reaction. Delta G and Rxn.
The enzyme typically does that. If you double the amount of enzyme present the delta G of a reaction will not change. G of the net reaction.
It only changes the activation energy. What is difference between delta G with and without enzyme. Makes the delta G negative B.
The catalysed reaction can be expressed as a series of many reactions and the overall G can be expressed as a sum of that of the individual reactions. The G for that reaction will be a negative value. Enzymes dont affect the delta G they only lower the activation energy.
Can enzymes alter the overall DELTA G for a reaction. Ad_2 This entry was posted in Answers and tagged decrease Delta enzymes reactions. 100 1 rating An enzyme does not effect delta G of a reaction.
Every chemical reaction involves a change in free energy called delta G G. It only changes the activation energy. In this reaction the.
Delta G naught means that the reaction is under standard conditions 25 celsius 1 M concentraion of all reactants and 1 atm pressure. What effect does enzyme have on delta G of the enzymatically catalyzed reaction. 2 takes it to transition state to maximize binding energy and breaks noncovalent bonds and releases energy.
The G for that reaction will be a positive value. Begingroup A catalyst does not change the free energy ie. If youre talking about a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme enzymes do not change K or delta G.
So as the chemical rxn approaches equilibrium delta G without the naught approaches zero. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy Ea or ΔG for a reaction. These are thermodynamic properties.
Exergonic reactions release free energy. Standard free energy change at pH 7-1 M for all-pH 7 Mg2 1 mM H2O 555 M. However delta G naught remains the same because it is still referring to when the rxn is at standard conditions.
Delta G naught prime means that the pH is 7 physiologic conditions everything else is the same. It only lower the activation energy of reaction Explain the relationships among the change in the degree of disorder the change in entropy the change of ethalphy and the change in free energy that occur during a chemical reaction. Makes a non-spontaneous reaction spontaneous C.
Therefore if you double the amount of enzyme present the reaction will speed up but the overall delta G will remain the same. Enzymes are specialized proteins that catalyze or speed up What is the difference between free energy and activation energy. The first law of thermodynamics.
K1 negative Delta G. So their difference the Delta G is the same. Enzymes are specialized proteins that catalyze or speed up chemical reactions.
Enzymes do not affect ΔG or ΔGo between the substrate and the product. Do enzymes change the delta G of the reaction. Reduces the difference in energy between the reactants and the products In step 2 of glycolysis Glucose-6-phosphate is transformed into fructose-6-phosphate pictured below.
Now I want to quickly point out that you may see delta G double dagger written out as EA in some textbooks. As the substrate enters the active site the enzyme changes shape slightly due to interactions between the substrates chemical groups and chemical groups on the side chains of the amino acids that form the active site. It remains unchanged when the enzyme acts on that chemical reaction but it affects activation energy.
Previous question Next question. If you double the amount of enzyme present the delta G of a reaction will not change. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Difference between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions How does enzyme lower activation energy. Maximal binding energy which will be released. We define ΔG0 pronounced delta.
View the full answer. The enzyme does not change the Gibbs free energy of the reaction.
Structural Biochemistry Enzyme Gibbs Free Energy Graph Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
Free Energy Endergonic Vs Exergonic Reactions Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Does an Enzyme Change the Delta G of a Reaction"
Post a Comment